WebSockets explained like a human!
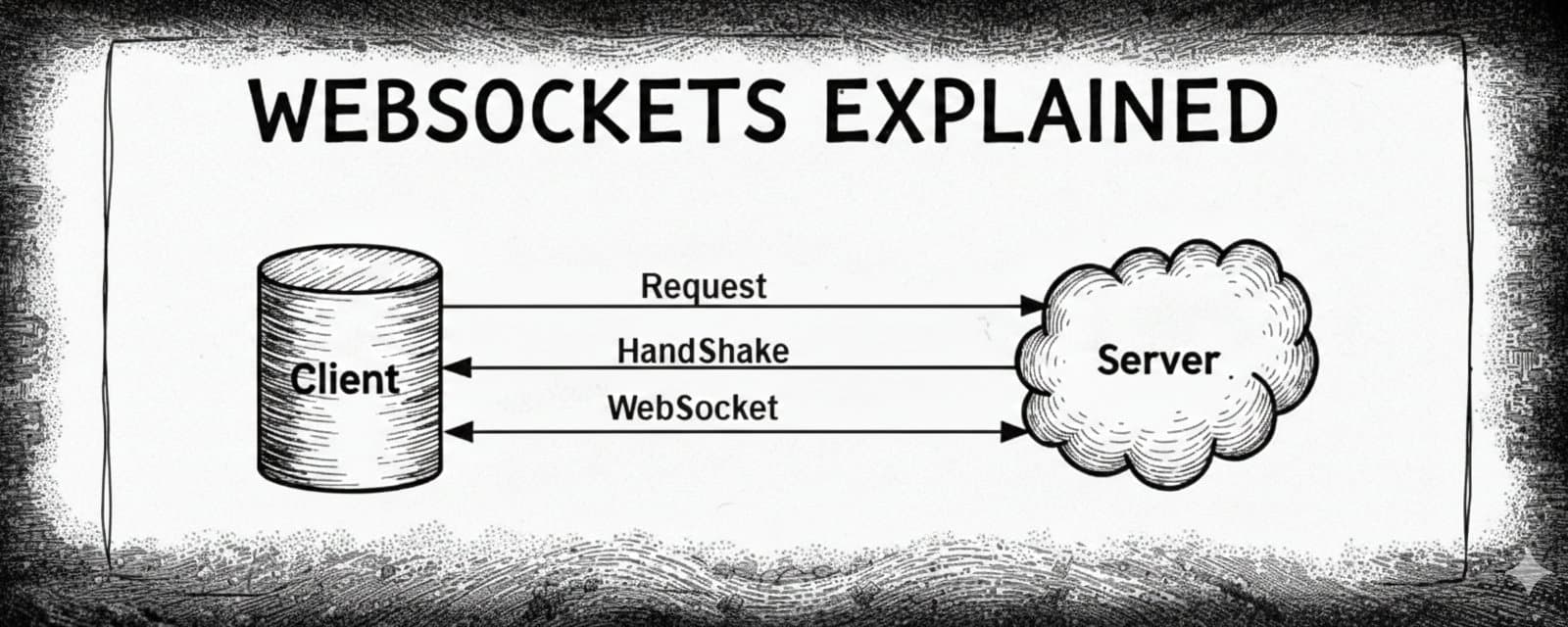
At some point, every web developer tries to build something “real-time” and ends up abusing HTTP.
Polling, long polling, weird and wild hacks.
This article is about that key technology which solves this problem… WebSockets, and I'll try to keep it beginner friendly because that's the aim.
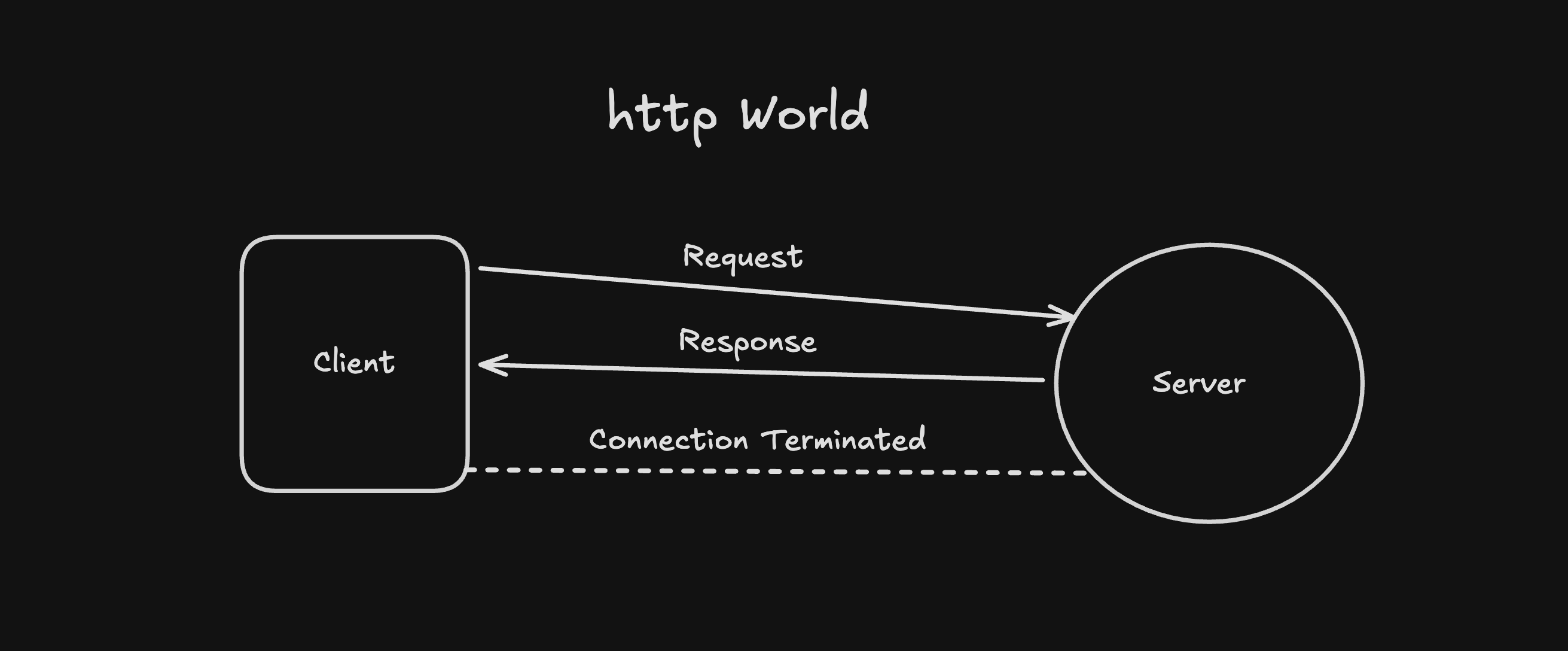
So if you’ve built web apps, you might be familiar with this flow:
- Browser asks for data
- Server responds with data
- Connection closes
This works great… until you want real-time updates, like chats, notifications, live dashboards, multiplayer games, and more. this is the point where HTTP starts feelign like the wrong tool. This is exactly why WebSockets exists.
1. The core problem with HTTP
- Client always initiates communication
- The server can't push data on it's own
- Every update needs a new request
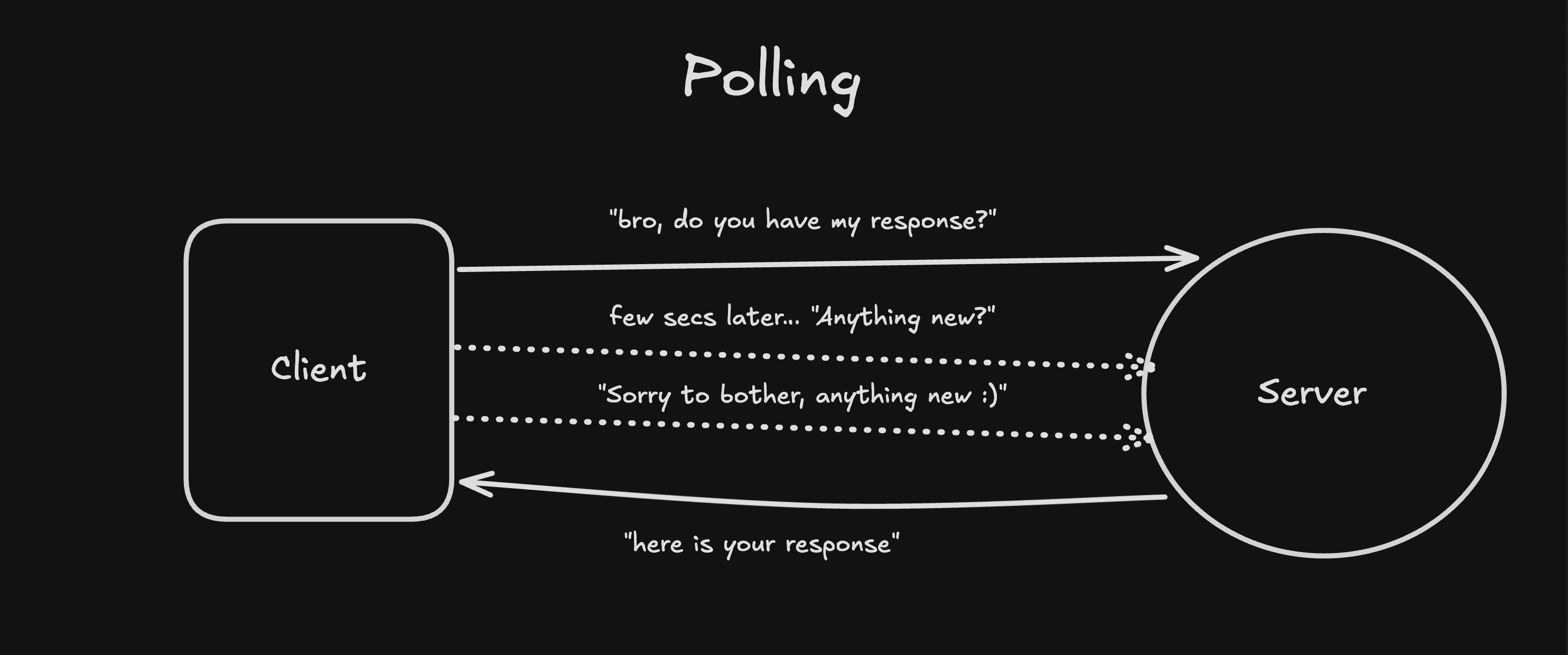
To fake "real-time" communication, developers usually try multiple methods, few of them being…
Polling
Clients keep asking the server every few seconds, until gets the output.
Long Polling
In long polling, the server holds the request open until something changes, better but still workaround.
Since here we're shooting server with multiple requests, and it's not an efficient solution when we're making something like a live dashboard, etc.
Hence, WebSockets were introduced.
2. What are WebSockets?
A WebSocket is a persistent, two-way connection between client and server, a full-duplex connection.
Once connected:
- The connection stays open
- Client and server BOTH can send messages anytime
- No repeated request–response cycle
Let me break it down with a simple analogy:
HTTP = emails Send → wait → reply
WebSockets = phone call. Both sides talk whenever they want
That’s it.
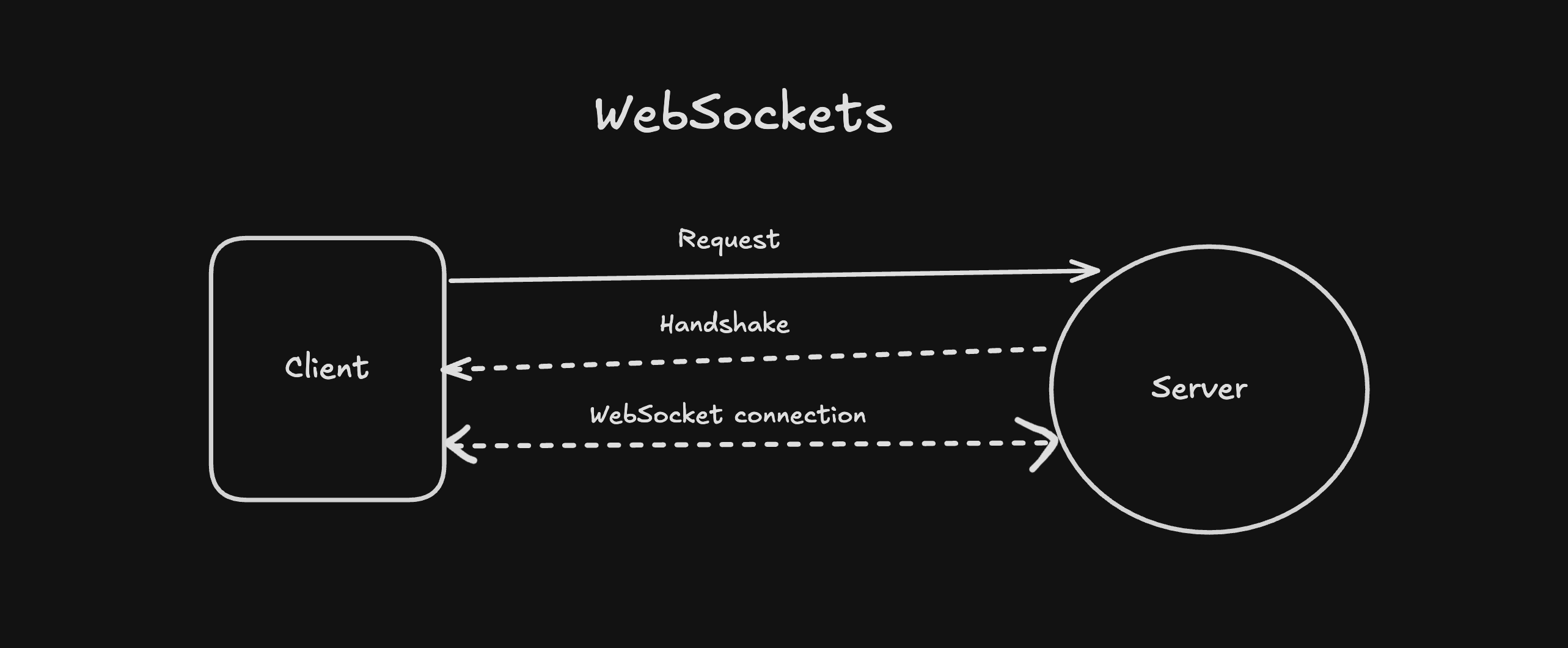
3. How a WebSocket connection starts
Important note for beginners… "WebSockets start as HTTP"
- Browser sends a normal HTTP request
- Requests an upgrade to WebSocket
- Server agrees
- HTTP steps aside, WebSocket takes over
After that, the connection stays open.
you don’t need to memorize headers… just remember it’s an upgrade. Below is an example of creating a WebSocket connection in pure JS.
// instantiating a new websocket
const socket = new WebSocket("ws://localhost:8080");
socket.onopen = () => {
console.log("Connected");
};
socket.onmessage = (event) => {
console.log("Message:", event.data);
};
socket.onclose = () => {
console.log("Disconnected");
};No fetch, No polling, No loops!
Once connected, the server can push data instantly.
Sending data from client
socket.send(
JSON.stringify({
type: "message",
text: "Hello server",
}),
);Most apps use JSON, but WebSockets don’t care, they just send bytes.
Using WebSockets in a React app
Here’s a clean React pattern most beginners can understand:
import { useEffect, useRef } from "react";
export default function Chat() {
const socketRef = useRef(null);
useEffect(() => {
socketRef.current = new WebSocket("ws://localhost:8080");
socketRef.current.onmessage = (event) => {
console.log("Message:", event.data);
};
return () => {
socketRef.current.close();
};
}, []);
const sendMessage = () => {
socketRef.current.send("Hello from React");
};
return <button onClick={sendMessage}>Send</button>;
}Key ideas:
- Use useRef to persist the socket
- Create connection once
- Clean up on unmount
Using WebSockets in a Next.js app is similar as we do in a React app, but make sure you never open a WebSocket connection in a server component ⚠️
3.1 Why WebSockets feel so fast?
There are a few reasons why WebSockets feel so fast:
- Persistent connection: No reconnecting for every message
- Minimal overhaed: No heavy http headers
- Full duplex: Client and server talk simultaneouly
3.2: When you SHOULD use WebSockets
Use them when any these is your priority:
- Updates must be instant
- Multiple users are involved
- Latency matters
3.3: When you SHOULDN'T
Avoid using WebSockets when the app is mostly static, making it real-time isn't the priority also if updates are rare.
The reason why I'm saying this is because they add complexity with reconnection logic, scaling challenges and more.
Hence, sometimes HTTP or SEE is enough
Now with WebSockets, many other topics are important to understand. Few of them being, "How do we actually use WebSockets in industries?", "How do we scale WebSockets?", "What are the potential challenges when using WebSockets?" and more…
I'm not going to cover those topics in the same article as I want to keep it generic and beginner friendly, if you want me to write upon that, let me know in the comments… and I'll be more than happy to talk over these things.
Well, from this let's also look at some common mistakes you can do as a beginner when using WebSockets:
- Using WebSockets for everything
- Forgetting reconnection logic and closing the connection
- Ignoring scale until it breaks
WebSockets are powerful but you must use them wisely.
Final Thought
WebSockets don’t make your app better by default. They make it more alive when used for the right reasons. Use them intentionally, understand their trade-offs, and they’ll serve you well.
With that set, i'll end this article. I encourage you all, to not just read this article, rather build something with this knowledge, break things and then only you'll get a better understanding.